Authentication Logs
This guide explains how to use the authentication logs feature in the admin panel. Authentication logs provide a detailed record of all login attempts, successful logins, and logouts, helping you monitor system access and identify potential security issues.
Accessing the Authentication Logs
- Log in to the admin panel with your administrator credentials
- Navigate to the Logs section in the sidebar
- Click on Authentication Logs to access the logs interface
Viewing Authentication Logs
The Authentication Logs page displays a table with all login activity in the system. The table includes the following information:
- User: The name of the user who attempted to log in, along with their role
- IP Address: The IP address from which the login attempt originated
- User Agent: The browser and device information of the login attempt
- Login At: The date and time when the login attempt occurred
- Login Successful: Whether the login attempt was successful
- Logout At: The date and time when the user logged out (if applicable)
- Cleared By User: Whether the session was cleared by the user
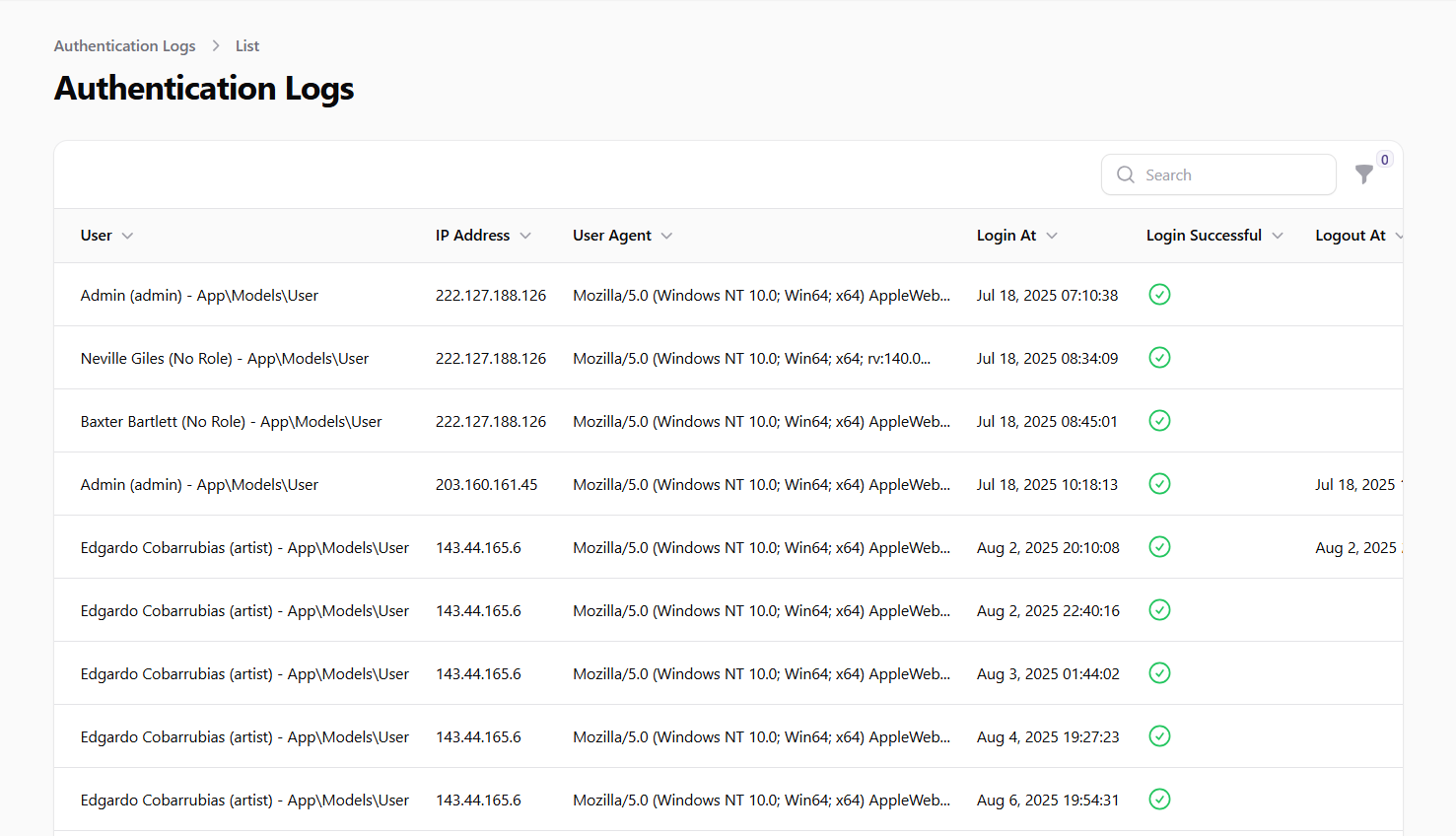 Screenshot: Authentication logs list view
Screenshot: Authentication logs list view
Understanding Log Entries
Each log entry provides valuable information about a login attempt:
User Information
The user column shows who attempted to log in, including their name and role (e.g., "John Doe (admin) - App\Models\User"). This helps you identify which accounts are being accessed.
IP Address
The IP address can help you:
- Identify the geographic location of login attempts
- Detect unusual access patterns
- Identify potential unauthorized access attempts
User Agent
The user agent provides information about:
- Browser type and version
- Operating system
- Device type (desktop, mobile, tablet)
This can help identify suspicious logins from unusual devices or outdated browsers.
Login Status
The "Login Successful" indicator shows whether the authentication attempt succeeded:
- ✓ (Green check) - Successful login
- ✗ (Red X) - Failed login attempt
Failed login attempts may indicate password guessing attacks or users who have forgotten their credentials.
Session Information
The "Logout At" and "Cleared By User" columns provide information about how the session ended:
- Logout At: When the user explicitly logged out
- Cleared By User: Whether the user manually cleared their session
Filtering Authentication Logs
You can filter the logs to focus on specific types of authentication events:
Filter by Login Success
- Use the Login Successful filter to show only successful logins
- This helps you see who has successfully accessed the system
Filter by Date Range
- Use the Login At filter to specify a date range
- Enter the start date in the Login From field
- Enter the end date in the Login Until field
- Click Apply to filter the logs
This is useful for investigating access during specific time periods or incidents.
Filter by Cleared Sessions
- Use the Cleared By User filter to show only sessions that were manually cleared
- This can help identify users who are security-conscious and properly end their sessions
Security Monitoring Best Practices
Authentication logs are a valuable security tool. Here are some recommended practices:
Regular Review
- Schedule regular reviews of authentication logs
- Look for patterns of failed login attempts
- Monitor logins from unusual locations or devices
Failed Login Investigation
When you see failed login attempts:
- Check if they're followed by successful logins (indicating a user who mistyped their password)
- Look for multiple failed attempts on the same account (potential brute force attack)
- Note unusual times of day for login attempts
IP Address Analysis
- Watch for logins from countries or regions where your users shouldn't be located
- Be alert to multiple accounts accessed from the same unfamiliar IP address
- Consider investigating logins from known VPN or proxy services if they're unusual for your users
User Agent Monitoring
- Be aware of logins from outdated browsers that might have security vulnerabilities
- Watch for unusual user agents that might indicate automated tools rather than legitimate browsers
Responding to Suspicious Activity
If you detect suspicious login activity:
- Investigate: Review the details of the suspicious logs
- Secure Accounts: Reset passwords for potentially compromised accounts
- Notify Users: Alert affected users about suspicious activity
- Block IPs: Consider blocking IP addresses with multiple failed login attempts
- Enable Additional Security: Consider implementing additional security measures like two-factor authentication
Important Notes
- Authentication logs are automatically generated and cannot be manually edited
- Logs provide valuable forensic information in case of a security incident
- Regular monitoring of authentication logs is a security best practice
- High volumes of failed login attempts may indicate a brute force attack
- Successful logins from unusual locations or at unusual times may indicate compromised credentials